Climate Change has a direct relationship with CO2. Why is too much CO2 in our atmosphere detrimental to planet Earth?
Greenhouse Gases
CO2 is a naturally occurring gas generated by significant levels of human activity. It is one of several greenhouse gases in our atmosphere including water vapour, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and halocarbons.
But how do these gases impact our planet? It all starts with the sun and a process called the Greenhouse Effect. The sun sends solar radiation to Earth in the form of light. About 30% of this radiation is deflected by the Earth’s atmosphere while the remaining 70% lands on the planet’s surface, in doing so this warms our land and oceans. The Earth subsequently thermally emits Infrared Energy and while some of it escapes the planet’s atmosphere the vast majority (about 90%) becomes absorbed and re-emitted by atmospheric gases. These atmospheric gases are called greenhouse gases and help to warm our planet and support life.
How Human Activities Influence our Climate
For millions of years, the production of greenhouse gases was regulated by the planet’s natural systems. Gases would be absorbed and emitted at a steady pace and the planet’s temperatures were regulated at consistent levels.
Human’s industry and development changed all of that. From the dawn of the Industrial Revolution in the latter half of the 1700’s, we have been generating additional greenhouse gases, primarily CO2, and releasing it into the atmosphere at an ever-increasing rate. This higher concentration of greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide in particular, is causing surplus heat to be trapped and global temperatures to rise.
Although there are several different types of greenhouse gases, CO2 represents over 80% of the greenhouse gases emitted as a direct consequence of human activity. Humans are currently generating around 30 billion tons of CO2 every year. The majority of this is caused by burning fossil fuels used for transportation and generating electricity with industrial processes and forestry contributing as well.
Scientific Consensus
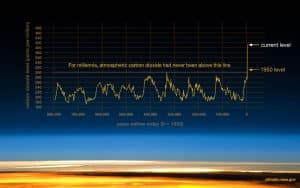
Leading climate scientists believe that to avoid the disastrous consequences of climate change that CO2 needs to reduce to levels of 350 parts per million (ppm). And, for context, figures from https://climate.nasa.gov/ revealed in 2020 that CO2 levels had reached 400 ppm for the first time in history. In 1960 CO2 levels were about 313 ppm and before the Industrial Revolution CO2 levels were about 270 ppm.
But it doesn’t stop there. CO2 affects our atmosphere but has also increased acidity levels in the planet’s oceans by around 30%, which is expected to rise. The consequences for aquatic organisms are severe.
Reducing CO2
Thankfully, technological advancements in renewable energy and energy-efficient technology have developed apace. By rapidly adopting technology that reduces our CO2 output and our over-reliance on CO2 generating fossil fuels – we can still save our planet and the environment.
At LUMENSTREAM our mission is to help the world’s largest energy users deploy energy-efficient technology at scale. We do this via our innovative “Pay as you Save” platform LED Lighting as a Service.
To learn how LUMENSTREAM can help your business reduce its carbon emissions please email us at info@lumenstream.com or call us on 0161 7111 343.


